发布时间:2022-05-10 09:52:36 来源: 浏览次数:895
译者:阿斯木江·阿不拉(新疆医科大学第一附属医院)
审校:宋光鲁(新疆医科大学第一附属医院)

Abstract
摘要
原
Objective: To compare the efficacy and safety of percutaneous polidocanol sclerotherapy and laparoscopic deroofing in the management of pediatric symptomatic simple renal cysts (SRCs).
译
目的:评价经皮聚桂醇硬化疗法和腹腔镜囊肿去顶治疗小儿有症状单纯性肾囊肿(SRCs)的疗效和安全性。
原
Methods: Forty-six patients with symptomatic SRCs (cyst size ≥4 cm) were treated either with polidocanol sclerotherapy (group A) or by laparoscopic deroofing (group B) between December 2009 and October 2019. The patients were reevaluated at 1, 6, and 12 months and annually thereafter.
译
方法:2009年12月至2019年10月期间,46例有症状的SRC患者(囊肿≥4厘米)接受经皮聚桂醇硬化疗法(A组)或腹腔镜去顶术(B组)治疗。分别在治疗后1、6和12个月进行疗效评估,此后每年进行一次。
原
Results: Twenty-one patients were treated with polidocanol sclerotherapy (group A) and 25 patients with laparoscopic deroofing (group B). The mean follow-up period was 58.7 months (14–107) in group A and 57.2 months (12–118) in group B. Complete regression was seen in 19 (90.5%) and 24 (96%) patients in groups A and B, respectively (p < 0.05). Partial regression was documented in one patient each in group A (4.8%) and B (4%).
译
结果:21 例患者接受聚桂醇硬化剂治疗(A 组),25 例患者接受腹腔镜去顶术(B 组)。平均随访时间A组为58.7个月(14-107),B组为57.2个月(12-118)。囊肿完全消退者A组19(90.5%) 例,B组24(96%)例 ,p<0.05),部分消退者A组(4.8%),B组(4%)各1例 。
原
In one group A patient, a laparoscopic deroofing was performed due to sclerotherapy failure after 27 months. The operation time, postoperative hospital stay, and cost were significantly less in group A than in group B (36.3 ±8.4 vs 96.9 ± 19.1, 19.7± 2.4 vs 56.0 ± 8.6, and U8173 ± 1343 vs U14,119±2021, respectively; p < 0.05).
译
A 组中1例随访27个月囊肿复发行腹腔镜囊肿去顶术。在手术时间、术后住院时间和住院费用方面A组显著低于B组(分别为36.3±8.4 vs 96.9±19.1、19.7±2.4 vs 56.0±8.6和U8173±1343 vs U14,119±2021;p < 0.05).
原
Conclusion: Polidocanol sclerotherapy and laparoscopic deroofing were found to be equally effective interventions associated with minimal complications for pediatric symptomatic SRCs. We recommend polidocanol sclerotherapy as the first option for children with symptomatic SRCs and laparoscopic deroofing in cases of failed polidocanol sclerotherapy.
译
结论:聚桂醇硬化疗法和腹腔镜囊肿去顶术治疗儿童有症状单纯性肾囊肿的疗效相当。推荐聚桂醇硬化疗法作为治疗小儿有症状SRC的首选治疗,硬化治疗后囊肿复发患儿建议行腹腔镜下囊肿去顶减压术治疗。
Introduction
介绍
原
A simple renal cyst (SRC) is quite common in adults, with the incidence increasing with age from >5% in the fourth decade to 36% in the eighth decade of life. However, it is uncommon in children with an approximate incidence between 0.22% and 0.55%.
译
单纯性肾囊肿(SRC)常发病于成年人,发病率可从40岁的>5%增加到80岁的36%左右。但是,SRC在儿童中的发病率并不高,发病率大约在0.22% ~ 0.55% 之间。
原
With the widespread use of ultrasonography (USG), SRC has been increasingly discovered in routine urologic practice. Bosniak’s CT scan classification is the reference for the diagnosis of SRC in adults. Pediatric SRC corresponds to Bosniak category I, which is a thin-walled, clear lumen with no echoes within the renal cyst.
译
随着超声检查 (USG) 的普及,SRC检出率逐渐增高。Bosniak的CT扫描分级可作为成人SRC诊断的参考。儿童的SRC相当于Bosniak I级,呈壁薄、囊液清,无回声囊腔。
原
SRC is asymptomatic in most children and is discovered incidentally. However, SRC may cause several symptoms, including flank pain, hematuria, hypertension, and pelvicaliceal system obstruction. Active treatment, including percutaneous aspiration (with or without injection of a sclerosing agent), endoscopic marsupialization or excision, open surgery, and laparoscopic deroofing, is recommended in symptomatic children.
译
大多数儿童SRC是无症状的,常为偶然发现。SRC会导致几种临床症状,如腰痛、血尿、高血压和肾盂肾盏梗阻。有症状儿童肾囊肿的治疗方法有:经皮抽吸(注射或不注射硬化剂)、内镜下开窗减压术或切除术、开腹手术和腹腔镜囊肿去顶术。
原
While aspiration and sclerotherapy are effective minimally invasive approaches, laparoscopic deroofing has gained popularity in recent years. Among various sclerosing agents used for symptomatic SRC, polidocanol is widely used and effective in the treatment of vascular malformations, esophageal and gastric varices, hydrocele, varicocele, and management of gastrointestinal bleeding apart from renal cysts.
译
尽管抽吸和硬化疗法是有效的微创治疗方法,然而腹腔镜囊肿去顶术近年来获得了广泛的使用,在治疗有症状SRC的各种硬化剂中,聚桂醇在血管畸形、食管胃底静脉曲张、鞘膜积液、精索静脉曲张、肾囊肿外的胃肠出血的治疗中应用广泛,疗效显著。
原
Although several clinical studies have focused on the diagnosis and treatment of SRC in adults, few studies have reported possible therapies of pediatric SRC, in particular, the comparison between sclerotherapy and laparoscopic deroofing and fewer long-term outcome analyses. Furthermore, no guidelines exist for the management of pediatric SRC.
译
尽管有关于成人SRC诊断和治疗的临床研究报道,但涉及儿童SRC的很少, 尤其是关于硬化疗法和腹腔镜囊肿去顶术治疗儿童SRC的疗效比较,并且远期结果分析也很少见。此外,还没有儿童SRC的诊疗指南。
原
Our study aimed to compare the long-term efficacy of polidocanol sclerotherapy with laparoscopic deroofing in pediatric symptomatic SRC and to evaluate the postoperative complications and safety of the two therapies.
译
我们旨在比较聚桂醇硬化疗法和腹腔镜囊肿去顶术对儿童有症状SRC的长期疗效,并评估两种治疗方式的术后并发症和安全性。
Materials and Methods
材料和方法
原
Study cohort
We retrospectively reviewed all symptomatic SRC cases between December 2009 and October 2019 in the Department of Urology of Shenzhen Children’s Hospital with long-term follow-up. A total of 46 patients with symptomatic SRC were treated by aspiration and sclerotherapy using polidocanol (group A, 21 patients) or laparoscopic deroofing (group B, 25 patients).
译
研究队列
我们回顾性分析了 2009 年 12 月至 2019 年 10 月在深圳市儿童医院泌尿外科住院有症状的SRC患者,并长期随访。共有 46 名有症状的 SRC 患者接受聚桂醇硬化治疗(A 组,21 名患者)或腹腔镜囊肿去顶术(B 组,25 名患者)治疗。
原
The study was conducted after obtaining permission from the Institutional Review Board of Shenzhen Children’s Hospital, and written informed consent was obtained from all patients before treatment.
译
本研究获得深圳市儿童医院机构伦理审查委员会许可,并且获得所有患者监护人的知情同意。
原
The patients were categorized into treatment groups. The indication for surgical treatment was SRC corresponding to symptomatic Bosniak stage I (thin-walled, clear lumen with no echoes within the cyst) that was symptomatic (flank pain, hypertension, hematuria, or obstruction of the pelvicaliceal system).
译
纳入标准:有症状(腰痛、高血压、血尿或集合系梗阻), Bosniak I 期(囊腔内薄壁、清晰、无回声)的 SRC。
原
Patients with complex cysts, polycystic kidney disease, cyst size<4 cm, and any history of treatment for cysts were excluded from the study.
译
排除标准:复杂囊肿、多囊肾病、囊肿大小<4cm以及有任何囊肿治疗史的。
原
All cysts were evaluated by renal USG and CT. Diagnosis of SRC was based on observation of Bosniak stage I criteria with good transmission leading to posterior enhancement and a well-demarcated posterior wall. The size, volume, and location of the cyst were measured by USG. One group A and two group B patients had parapelvic cysts.
译
所有患者经USG和CT进行评估。SRC的诊断基于对 Bosniak I 期的诊断标准,囊壁界限分明和后壁回声增强。通过USG测量囊肿的大小、体积和位置。A 组一例和B组2例为肾盂旁囊肿。
Surgical procedure
外科手术
原
General anesthesia was induced for group A patients, and an 18-gauge puncture needle was inserted via USG guidance into the cyst. Approximately 10–20 mL of fluid aspirate was taken for cytologic and biochemical examination, followed by equivalent volume injection of water-soluble contrast medium, to observe the cyst outline.
译
A组患者行全身麻醉,经USG引导将18号穿刺针插入囊肿。抽取约10-20mL液体进行细胞学和生化检查,随后注入等体积的水溶性造影剂,观察囊肿轮廓。
原
If the cyst did not communicate with the pelvicaliceal system and contrast medium showed no extravasation outside the cyst wall, the cystic fluid was aspirated completely. After aspiration, 1% polidocanol for 10% of cyst volume (not exceeding 20 mL) was instilled into the cyst, without further aspiration or sclerosant drainage.
译
如果囊肿没有与集合系统相通,未见造影剂外渗,则将囊液吸尽。抽尽囊液后,抽取囊液10%体积的1%聚桂醇(不超过20mL)注入囊腔内,不需要进一步抽吸或引流。
原
In group B, a peritoneal laparoscopic approach with three ports was used. All patients were placed in the flank position under general anesthesia. The first laparoscope port was placed at the upper edge of the umbilicus, and other two were introduced above and below the umbilicus along the midabdominal line.
译
在 B 组中,使用了三孔法腹腔镜技术。所有患者均在全麻下取仰卧位。第一个腹腔镜孔放置在脐上缘,另外两个沿中腹线在脐上方和下方。
原
A pneumoperitoneum was induced using the Hassan technique, and the colon and renal capsule were exposed. If the cyst was located in the posterior part of the kidney, the anterior part of the kidney was suspended for traction to expose it. The wall of the SRC was excised 0.5 cm above the junction of the wall and renal parenchyma. The perinephric omentum or fat was interposed into the capsule cavity to prevent recurrence (Fig. 1).
译
使用 Hassan 技术建立气腹,暴露结肠和肾包膜。如果囊肿位于肾脏的背侧,则将肾脏的腹侧悬吊进行牵引使其暴露。SRC壁在肾实质距0.5cm处切除。囊腔内置入肾周网膜及脂肪防止复发(图1)。
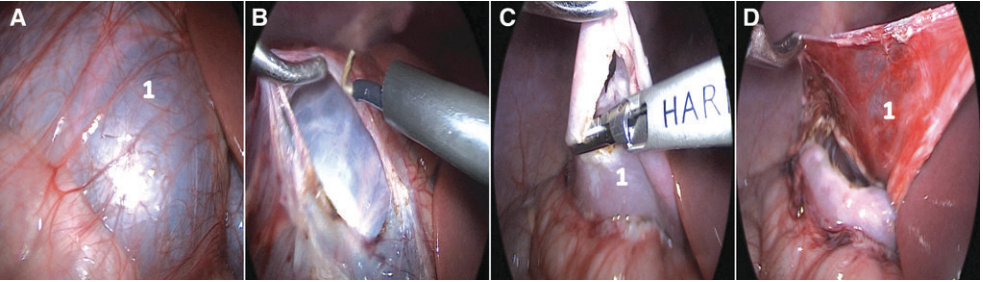
图片 1. 腹腔镜去顶术中显示右侧单纯性肾囊肿的术中图像。(A) A1,肾囊肿。(B) 结肠和肾包膜打开后暴露肾囊肿。(C) C1,切除部分囊壁。(D) 肾周组织。将肾周组织填入囊腔。彩色图像可在线获取。
原
At the same time, the connection between the bottom of the cyst and the collecting system was checked to exclude the possibility of caliceal diverticulum. For a parapelvic cyst, the hilum of the kidney was carefully dissected, and the structures were identified before treatment. The technique is demonstrated in the Supplementary Video S1.
译
同时检查囊肿底是否与集合系统相通,排除肾盏憩室。对于肾盂旁囊肿,仔细游离肾门组织,切除囊肿前确定其同肾门组织的解剖关系。该技术在补充视频 S1 中进行了演示。
Follow-up cohort
后续队列
原
The patients were reevaluated at 1, 6, and 12 months, and annually after treatment. The effect of the treatment was assessed by disappearance of symptoms and comparison of the recurrent cyst volume with the pretreatment cyst volume by USG. Success was defined clinically and anatomically as ‘‘complete regression,’’ with symptom disappearance and cyst size reduction >90%, whereas ‘‘partial regression’’ was defined as symptomatic relief with 50%–90% reduction in cyst volume. Failure was defined as<50% reduction of pre-treatment cyst volume and/or persistence of symptoms after treatment.
译
患者分别于治疗后 1、6 和12个月进行疗效评估,以后每年进行一次。按照症状是否消失,囊肿体积变化程度评估疗效。治愈:临床症状完全消失和影像学上囊肿体积缩小> 90%;好转:囊肿体积缩小50%–90%,症状缓解;无效:治疗后囊肿体积缩小<50%和/或治疗后症状持续存在。
Statistical analysis
统计分析
原
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 22.0 for Windows. Categorical variables are presented as the number of cases and percentages and compared using the chi-square test. Continuous variables that follow a normal distribution are described as means with standard deviations and compared using the Student’s t-test. A p-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
译
使用 SPSS 22.0 for Windows 进行统计分析。分类变量表示为病例数和百分比,并使用卡方检验进行比较。遵循正态分布的连续变量被描述为标准差均值,并使用Student’s-test进行比较。p值<0.05被认为具有统计学意义。
Results
结果
原
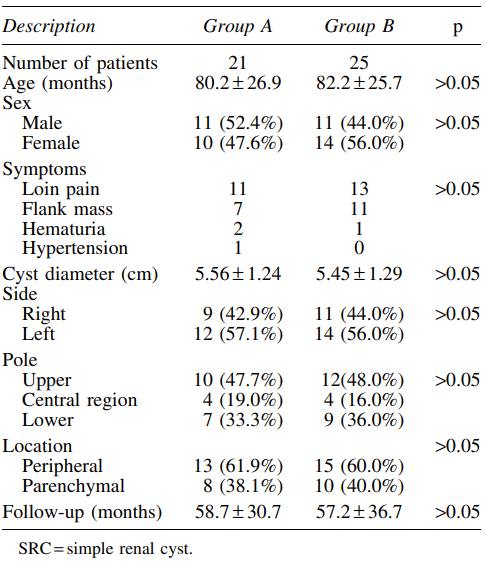
The mean age was 80.2 months (42–135) in group A (aspiration and polidocanol sclerotherapy) and 82.2 months (39–139) in group B (laparoscopic deroofing). The mean cyst diameter was 5.56 cm (range: 4.1–9.8) in group A and 5.45 cm (range: 4.2–10.2 cm) in group B. The mean follow-up period was 58.7 months (range: 14–107) and 57.2 months (range: 12–118) in groups A and B, respectively.
译
A组的平均年龄为80.2个月(42-135),B组的平均年龄为82.2个月(39-139)。A组的平均囊肿直径为5.56cm(4.1-9.8cm),B组为5.45cm(4.2–10.2cm)。A组和B组的平均随访时间分别为58.7个月(14-107个月)和57.2个月(12-118个月)。
原
Patients’ demographic characteristics and cyst locations are summarized in Table 1. Of these cysts, 60.6% were peripheral. The complete regression rates of SRCs were 8.7%, 60.9%, and 89.1% at 1, 6, and 12 months after treatment, respectively.
译
患者的人口基线资料和囊肿位置汇总见表1。其中,60.6%的囊肿为外突性囊肿。在治疗后1、6和12个月,SRCs的完全治愈率分别为8.7%、60.9%和89.1%。
表 1. 组间比较
A(注射聚桂醇硬化疗法)和 B 组(腹腔镜去顶减压术)
在 SRC 患者的人口学、临床和病理学特征
原
In group A, none of the patients had infection after aspiration, and two children had transient nausea, which resolved spontaneously. Cytologic examination was negative for malignancies in all patients, and biochemical analysis results were similar to plasma.
译
A组有一例患者抽吸后发生感染,2例出现一过性恶心,均缓解。所有患者的细胞学检查均为阴性,生化分析结果与血浆相似。
原
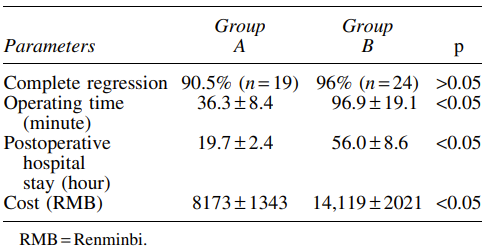
The mean operation time in group B was significantly higher than that in group A (96.9 vs 36.3 minutes) (p < 0.05) (Table 2), and the mean hospital stay after the procedure was significantly higher in group B [56.0 (range: 48–72) hours] than in group A [19.7 (range: 16–24) hours].
译
B组的平均手术时间显著高于A组(96.9vs36.3min)(p<0.05)(表2),B组术后平均住院时间[56.0(48-72)小时]显著高于A组[19.7(16-24)小时]。
表 2. 结果:A 组(抽吸和聚桂醇硬化疗法)与 B 组(腹腔镜去顶术)
原
In group A, complete and partial regression was achieved in 19 (90.5%) and 1 (4.8%) case, respectively. One patient with complete regression had a parapelvic cyst. One patient gradually developed occasional abdominal pain, and ultrasound showed the volume of the recurrent cyst to be 75% of the pretreatment volume at 19 months after therapy. At the 27th month of follow-up, persistent pain was reported, and the cyst volume relapsed to 90% of the pretreatment volume. Laparoscopic treatment led to pain relief and significant reduction in cyst volume.
译
A组19例(90.5%)治愈,1例(4.8%)好转。1例肾盂旁囊肿完全治愈,一例患者术后有偶尔的腹痛。超声显示第19个月时囊肿体积为治疗前75%。第 27 个月时患者出现持续疼痛,囊肿体积复发至治疗前体积的 90%。采用腹腔镜囊肿去顶术治疗后治愈。
原
In group B, complete and partial regression was achieved in 24 (96%) and 1 (4%) patient, respectively, without need for further open surgery. Two patients with complete regression had a parapelvic cyst. There was no significant difference in complete regression or complications between groups A and B. Group A had lower treatment costs than group B (U8173 ±1343 vs U14,119 ±2021), although most of the costs were paid by medical insurance.
译
在B组中,有24例治愈(96%)和1例(4%)好转,其中2例为肾盂旁囊肿。A组和B组在治愈率和术后并发症方面相当。A组的治疗费用低于B组(U8173±1343 , U14,119±2021)。
Discussion
讨论
原
The majority of simple cysts encountered in practice are developed in otherwise normal kidneys. Compared with older patients, younger patients undergo rapid cyst enlargement, with an average size increase of 0.3–1.6 mm and average growth rate of 1%–3.9% per year. Mechanical effects of space-occupying lesions are more likely to occur due to large cysts.
译
大多数单纯性囊肿都是在正常肾脏中发生发展而来的。与老年患者相比,年轻患者肾囊肿比老年患者生长速度更快,每年增加约0.3–1.6 mm(1%–3.9%)。体积大的肾囊肿患者更容易出现压迫症状。
原
A small proportion of adults with SRC have symptoms, pain being the most common. Hypertension, hematuria, flank mass, and cyst rupture are not common. In children, loin pain is the most common symptom, followed by flank mass (Table 1).
译
成人SRC,最常见的症状是疼痛,高血压、血尿、腹部包块,而囊肿破裂极其罕见。在儿童中,腰痛是最常见的症状,其次是腹部包块(表1)。
原
Possible reasons for different incidence of flank mass in children compared with adults with SRC are as follows: (1) SRC grows more quickly in children; (2) in the present study, most cysts were peripheral (>60% in our study) and the abdominal wall of children is thin, which could be noticed by patients or caregivers.
译
儿童SRC发现腹部包块比成人高的原因可能是:(1)SRC在儿童中生长更快;(2) 在目前的研究中,大多数囊肿是外周的(在我们的研究中>60%),儿童的腹壁很薄,患者或护理人员更容易观察到。
原
Several treatments have been proposed to manage symptomatic SRC. Aspiration without sclerotherapy has a high recurrence rate because the cysts are lined by secretory epithelium. Aspiration with sclerotherapy has been reported to have a much higher success rate. Sclerosing agents destroy the cyst wall cells and induce local inflammation on the cyst luminal surface, leading to cystic wall adhesion and cyst reduction or resolution.
译
目前已有报道一些治疗SRC的治疗方式。不注入硬化剂的抽吸法有很高的复发率,因为囊肿内壁细胞有分泌功能。研究报道采用抽吸后硬化剂治疗有很高的治愈率。硬化剂可以破坏囊壁细胞并在囊腔表面诱导发生炎症反应,导致囊壁粘连使囊肿体积缩小和消退。
原
Bean first reported the treatment of symptomatic SRC with 95% alcohol during diagnostic aspiration, followed by sterile ethanol (95%–99%). Possible side effects included fever, nausea, pain, and occasionally serious complications, such as aseptic psoas abscesses and central nervous system depression.
译
Bean 首次报道了用 95% 酒精治疗有症状的SRC,随后使用了无水乙醇(95%–99%)治疗。其副作用包括发烧、恶心、疼痛,偶尔还会出现严重并发症,如无菌性腰大肌脓肿和中枢神经系统抑制。
原
The ideal sclerosing agent should be safe and effective. To overcome the shortcoming associated with the use of alcohol as a sclerosing agent, several other sclerosing agents, including bismuth phosphate, acetic acid, povidone/iodine, polidocanol, Pantopaque, minocycline hydrochloride, and ethanolamine oleate, have been used for percutaneous sclerotherapy with varying degrees of success.
译
理想的硬化剂应该是具有安全性和有效性。为了减少酒精使用相关的副作用, 应用于经皮硬化疗法SRC的其它硬化剂有磷酸铋、乙酸、聚维酮/碘、聚桂醇、盐酸米诺环素和油酸乙醇胺,都取得不同程度的疗效。
原
Polidocanol consists of 95% hydroxypolyethoxydodecane and 5% ethyl alcohol, and it has a detergent action that produces a rapid overhydration of the cells, with consequent destruction. Aspiration and percutaneous polidocanol sclerotherapy offer a high success rate in the treatment of SRC without the need for repeated interventions associated with sclerotherapy performed with ethanol.
译
聚桂醇由95% 羟基聚乙氧基十二烷和 5% 乙醇,它是一种清洁类硬化剂,具有使细胞蛋白质析出,从而导致细胞破坏。经皮抽吸和注入聚桂醇硬化疗法治疗SRC有很高的治愈率。
原
Ohta et al. and Agarwal and coworkers reported an efficacy of 93% and 90%, respectively, with this treatment for renal cysts in adults. In addition, compared with conventional agents such as phenol and ethanol, polidocanol is safer for the treatment of SRC.
译
Ohta 等人和 Agarwal 报告道,用此法治疗成人SRC的治愈率为93%和90%,与苯酚和乙醇等常规药物相比,聚桂醇治疗 SRC 更安全。
原
Longer contact time between the sclerosant and renal cyst epithelium has been suggested for higher success rates. We effectively used 1% polidocanol, retaining it within the cyst to prolong the contact time for adequate sclerosis of the cyst walls. In addition, the dosage of the sclerosing agent may also affect the outcome of SRC.
译
硬化剂和肾囊肿上皮之间的接触时间越长,治愈率越高。我们使用了1%聚桂醇,将其保留在囊肿内,以延长接触时间,使囊壁充分硬化。此外,硬化剂的剂量也可能影响SRC治疗的结果。
原
Yonguc and associates reported that using 1% polidocanol in an amount equal to 2% of cyst volume had a low regression rate (65.1%). However, we used 1% polidocanol in an amount equal to 10% of cyst volume, which had been proven to have a high success rate. Similarly, SRC therapy in adults was reported to be safe, with efficacy as high as 90%, by Agarwal and colleagues We propose that the therapeutic effect of SRC is dose dependent.
译
Yonguc 等报道,使用相当于 2% 囊肿体积的 1% 聚桂醇治愈率 (65.1%)。然而,我们使用了约 10% 囊肿体积的 1% 聚桂醇,具有很高的成功率。Agarwal 等,同样方法治疗成人 SRC是安全的,治愈率高达 90%。因此我们认为 SRC 的治疗效果具有剂量依赖性。
原
Most group A patients had complete or partial resolution after aspiration and polidocanol sclerotherapy (Table 2). No further intervention was required in case of continuous SRC remission. In cases of recurrence, the residual cyst was excised laparoscopically. Aspiration and sclerotherapy of SRC were rarely accompanied by significant complications, consistent with our study findings. One of our patients with failed sclerotherapy was treated laparoscopically.
译
本研究中 A 组大部分患者在抽吸和聚桂醇硬化治疗后完全或部分消退(表 2)。如果硬化治疗失败,囊肿复发可以用腹腔镜下切除残留囊肿。4抽吸和硬化剂治疗SRC很少出现明显的并发症,与我们的研究结果一致。我们的1例硬化剂治疗失败的患者接受了腹腔镜囊肿去顶术治疗。
原
Camacho and associates reported that extravasating the sclerosing agent into the peripelvic tissue caused fibrosis of the ureteropelvic junction in cases of parapelvic cysts. While some researchers do not recommend sclerotherapy for parapelvic cysts, Agarwal and associates reported the same to have satisfactory results without procedure-related complications.
译
Camacho 等报告,抽吸和硬化剂治疗肾盂旁囊肿患者,硬化剂外渗到腹腔周围组织会导致输尿管腹腔交界处的纤维化。虽然学者不建议对肾盂旁囊肿患者进行硬化剂疗法,但Agarwal 等报告,抽吸和硬化剂治疗肾盂旁囊肿依然有效,没有出现相关并发症。
原
We found complete regression in one patient with parapelvic cysts treated by sclerotherapy. This may be due to the benefit of general anesthesia avoiding random intraoperation position changes due to pain, thus ensuring complete injection of polidocanol into the capsule cavity only, under ultrasonographic guidance.
译
本研究中我们也有相同发现。为了避免患者因穿刺疼痛而导致囊肿位置发生变化,我们建议在超声引导和监控下确保将聚桂醇完全注入囊腔内。
原
Since 1989, laparoscopy has gained wide acceptance for SRC, being minimally invasive with higher success rates than open surgery, as reported in previous studies. Agarwal and associates reported laparoscopic deroofing surgery as a safe and effective treatment for symptomatic SRC. We found laparoscopic deroofing to be effective for the treatment of pediatric SRC.
译
自 1989 年以来,腹腔镜囊肿去顶手术已被广泛应用,具有微创、成功率高的优点。Agarwal 等报告,腹腔镜囊肿去顶手术治疗有症状SRC是一种安全有效的微创方法。我们发现此术式治疗小儿 SRC 是同样有效的。
原
The procedure not only removed part of the cyst wall but, more importantly, also drained the cyst adequately. In addition, we observed that maximal removal of the cyst wall during the operation could further reduce the recurrence of cysts. No serious complications were seen following laparoscopic treatment in our study.
译
该手术不仅去除了部分囊壁,更同样重要的能充分引流囊液。我们观察到最大限度地去除囊壁可以进一步减少囊肿的复发。本研究中腹腔镜组未出现严重术中、术后并发症。
原
All patients with SRC in our study were symptomatic, and most of the symptoms were relieved following intervention. Long-term follow-up showed that both therapies had few complications and equal efficacy in these children. In addition, we found that parapelvic cysts can also be treated easily by either technique.
译
另外,所有有症状SRC患者治疗后大部分症状得到缓解。本研究中长期随访结果,这两种方法治疗儿童有症状SRC疗效相同。此外,我们认为肾盂旁囊肿也可以通过这两种技术治疗。
原
Outpatient aspiration and sclerotherapy are performed without analgesics, in adults. However, it is not suitable for children because changes in body position pose risk of damage to the surrounding organs. Consistent with the reports of some previous studies, aspiration and sclerotherapy were found to have the advantages of minimal hospitalization and lower costs than laparoscopic surgery of SRC.
译
在成人SRC进行抽吸和硬化剂治疗可以在门诊不适用止痛药的情况下进行,但是,儿童SRC却不行,因为疼痛会使体位变化,增加造成周围器官损伤的风险。与以前的一些研究一致,抽吸和硬化疗法结果比腹腔镜手术具有住院时间短和费用低的优点。
原
Long-term follow-up is recommended after initial treatment of SRC, especially in case of residual cysts. Skolarikos et al. reported that complete resolution might take as long as 6–12 months after treatment, and residual cysts observed during this period do not signify recurrence or failure.
译
建议SRC患者在初次治疗后进行长期随访,特别是在囊肿未消退的情况下。Skolarikos 等报道,囊肿治疗后可能需要6-12个月才能完全消退,如在此期间还能发现囊肿并不意味着复发或失败。
原
After a median follow-up of 22 months, Dell’Atti observed persistent lumbar pain in some patients following sclerotherapy. Okeke et al. followed patients for a mean of 17 months and observed pain recurrence in five patients originally managed by sclerotherapy.
译
在随访 22 个月后,Dell'Atti观察到一些硬化剂治疗后的患者出现持续腰痛。Okeke等对患者进行17个月的随访,发现有5例患者在初次硬化剂治疗后出现疼痛复发。
原
In our study, one case had failed sclerotherapy after a follow-up of over 2 years. The follow-up of patients is ongoing, and there has been no recurrence after laparoscopic deroofing.
译
本研究中1例患者硬化剂治疗随访2年后,囊肿复发,行腹腔镜囊肿去顶术后治愈。
原
Several studies have shown the safety and efficacy of the sclerotherapy or laparoscopic procedure in adults, but few studies have focused on the management of pediatric SRC. The management of pediatric SRC varies widely, with imprecise surgical indications. Based on our study, we recommend reliable indications for surgical therapy for pediatric SRC to be loin pain, flank mass, hematuria, and other symptoms due to SRC.
译
相关研究已证明成人硬化疗法或腹腔镜手术的安全性和有效性,但研究儿童 SRC 治疗的很少。由于儿童 SRC 的治疗差异很大,手术适应症不明确。我们推荐小儿 SRC 手术治疗的适应症是腰痛、腰腹部肿块、血尿和其他 SRC 引起的症状。
原
Although both methods had equal efficacy in children, laparoscopy was more invasive with more potential complications. Once a diagnosis of symptomatic SRC is established in children, aspiration and polidocanol sclerotherapy can be chosen as the initial treatment, with laparoscopic intervention subsequent to treatment failure.
译
虽然这两种方法在儿童中的疗效相同,但腹腔镜手术的侵入性更大,潜在的并发症也更多。在确诊为有症状儿童SRC时我们建议,可以选择抽吸和聚桂醇硬化疗法作为首次治疗,在治疗失败后行腹腔镜干预。
原
Our study describes the first efficacy comparison between polidocanol sclerotherapy and laparoscopic deroofing in a pediatric SRC cohort. Being a nonrandomized series, our study has limitations. A larger randomized comparison of sclerotherapy and laparoscopic procedures with longer follow-up could further validate the two methods.
译
我们是首次评价聚桂醇硬化疗法和腹腔镜囊肿去顶术治疗儿童有症状SRC疗效的研究,作为一个非随机系列研究,我们的研究有局限性。需要更大的样本量和更长的随访时间来验证这两种方法治疗儿童有症状SRC的疗效。
Conclusion
结论
原
Aspiration and polidocanol sclerotherapy, and laparoscopic deroofing are effective interventions with minimal complications, for the effective clinical and anatomical management of symptomatic pediatric SRC. Advantages of aspiration and polidocanol sclerotherapy are minimal invasiveness, shorter hospitalization, and cost-effectiveness compared with laparoscopic deroofing. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous aspiration and polidocanol sclerotherapy of symptomatic SRC should be the first-line treatment followed by laparoscopic deroofing in case of sclerotherapy failure.
译
抽吸和聚桂醇硬化疗法以及腹腔镜去顶手术是治疗儿童有症状SRC有效的干预措施,并且并发症最少,能缓解患者的临床症状和消退囊肿。与腹腔镜去顶术相比,抽吸和聚桂醇硬化疗法具有侵入性小、住院时间短、费用低的优点。对于有症状的 SRC,超声引导下经皮穿刺和聚桂醇硬化治疗应作为首选治疗,当治疗失败时,应采用腹腔镜去顶术。
(译文仅供学习交流使用)